Hiring remote developers offers unparalleled benefits, from accessing top-tier talent across the globe to ensuring your operations continue seamlessly regardless of local disruptions. However, this model also presents unique security challenges that if unaddressed, could turn into vulnerabilities leading to unauthorized access, data breaches, and other cybersecurity nightmares.
One of the primary concerns is the security of the networks remote developers use. The comfort of accessing corporate systems from one’s own home or a coffee shop comes with the increased risk of exposing sensitive data to unsecured or improperly secured networks. Additionally, the lack of control over physical devices and potential susceptibilities to social engineering scams can put your digital assets at grave risk.
However, there’s no need to worry! With a strong security strategy in place, you can tackle these challenges and create a thriving, secure remote development team. This article will delve into the best practices to reduce risk and ensure remote work benefits both businesses and developers alike.
A Robust Strategy for a Secure Remote Environment
To mitigate these risks and maintain the integrity of your digital ecosystem, implementing a comprehensive security strategy is critical. Here are several key practices to ensure your remote development team works securely:
1. Implement Basic Cybersecurity Best Practices
Start by teaching all team members, both in-house and remote, the basics of cybersecurity. This includes identifying phishing attempts, using up-to-date antivirus software on their devices, and recognizing the importance of regular software updates.
By taking a few simple steps and adopting straightforward security practices, you can significantly enhance remote information security at your company. Implementing security measures, from ensuring software is always updated to instilling vigilant habits like monitoring work devices constantly, can make a big difference.
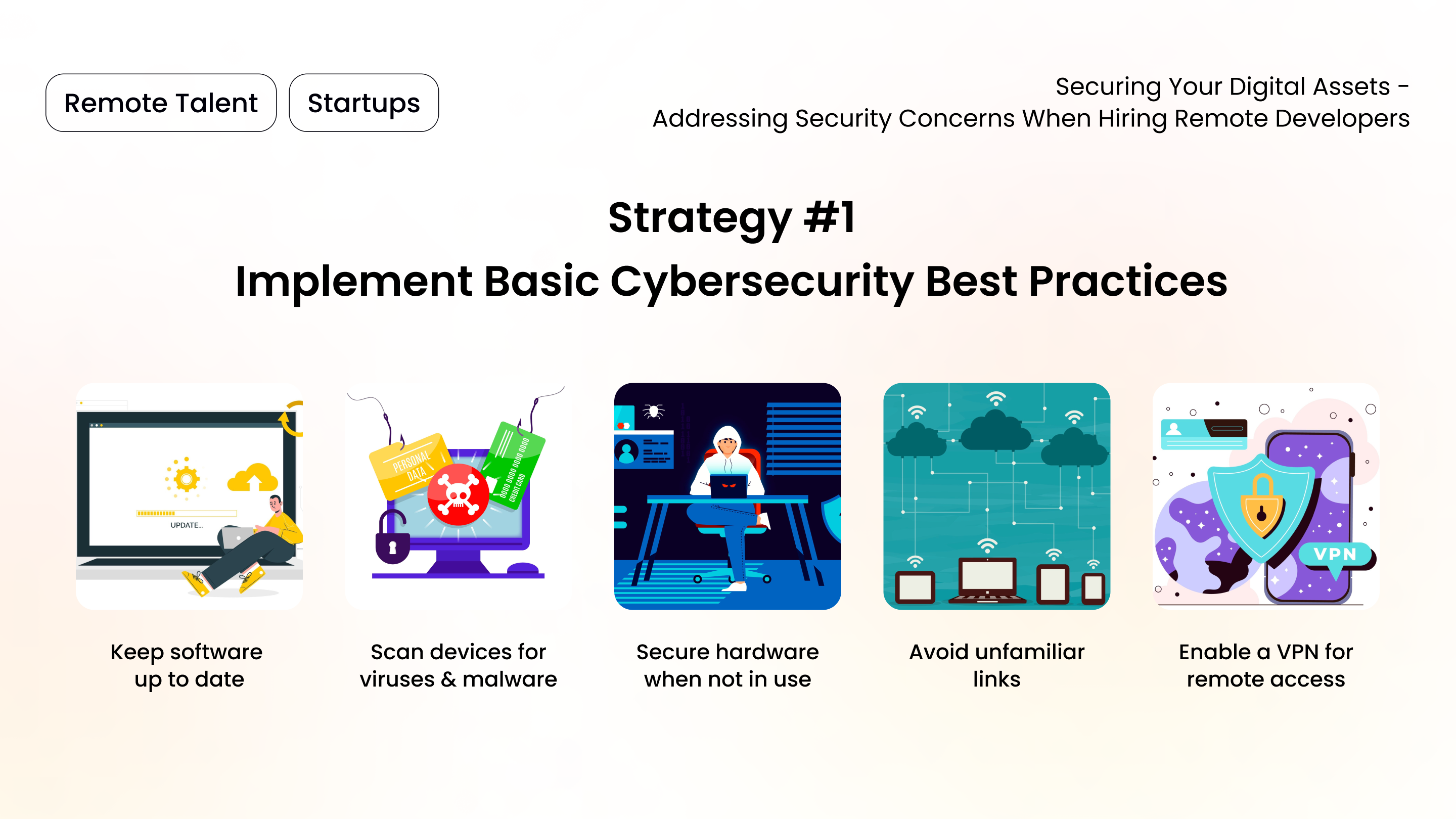
- Keep software up to date: Mandate automatic updates for operating systems and software applications to protect against new threats.
- Scan devices for viruses and malware: Utilize reputable antivirus and anti-malware software for an added layer of security on well-maintained devices.
- Secure hardware when not in use: Educate remote team members to never leave their work devices, including personal ones used for work, unattended in public spaces.
- Avoid unfamiliar links or links from unknown senders: While email services filter spam, one should never open links or attachments from unknown origins.
- Only use trusted Wi-Fi networks: Be wary of public Wi-Fi networks, which might be fraudulent and put users at risk.
- Enable a VPN for remote access: A virtual private network (VPN) adds a secure layer when connecting to company networks remotely.
If your company deals with personally identifiable information (PII), adhere to additional practices to secure data and prevent breaches, in line with privacy laws like the GDPR.
2. Secure Home and Remote Office Networks
Encourage remote developers to enhance their home network security by:
- Managing Sensitive Data Carefully
- Utilizing a VPN for secure connections.
- Encrypting their Wi-Fi with WPA2 or WPA3.
- Changing default router passwords to strong, unique options.
Additionally, ensure you’re only connecting to known and secure Wi-Fi networks. Here’s how to keep your network secure, according to the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA):
- Use a secure password, updated regularly.
- Customize your service set identifier (SSID).
- Limit network access to specific users, each with a unique access password.
- Encrypt with WPA3 for optimal security of data in transit.
- Install a firewall on your router or modem.
These steps drastically lower the risk of unauthorized access, potential breaches, attacks, or data leaks.
Remote team members should pledge to access work documents only over secure networks, avoiding the free public Wi-Fi in places like coffee shops, libraries, and airports due to inadequate security standards.
Unsecured networks expose you to data privacy issues, malware, and man-in-the-middle attacks. Limit access to sensitive data based on roles and necessity. Use end-to-end encryption for data in transit and at rest, ensuring that only authorized individuals can access the information they need to perform their job.
3. Keep Communication Secure
Adopt secure platforms for team communication that offer end-to-end encryption to minimize the risk of confidential information being intercepted during transmission. However, connecting to a secure network and granting role-based permissions will not suffice if your team discusses work or shares files through insecure channels. It’s crucial to ensure that all communications, especially with remote team members, are conducted securely.
Instead of allowing team members to access documents and send work-related messages through personal email accounts and phones, it’s advisable to provide your team with secure, company-issued phones.
If issuing company phones is not feasible or if you have embraced a bring-your-own-device (BYOD) policy, there are still several measures you can take to enhance the security of your work communications. These include assigning company email addresses to all team members and ensuring the use of end-to-end data encryption, utilizing encrypted messaging applications like Signal for sensitive conversations, keeping all work-related communications confined to a company-controlled app such as Slack to prevent data leaks, and only sharing files through approved channels like a corporate Google Drive account.
Furthermore, when communicating with independent talent or contractors, it’s beneficial to use a dedicated platform like Upwork Messages, which is designed to protect both parties’ communications. By implementing these strategies, you can significantly improve the security of team communications and protect your organization’s confidential information.
4. Develop a Strong Password Policy
Remote working arrangements heighten the difficulty of ensuring developers adhere to optimal password practices. Organizations should thus implement strategic measures to bolster security. A widely recommended approach involves mandating the periodic update of passwords for work-related applications. By requiring a password reset every few months, the risk of account breaches post-credentials leak significantly diminishes, as the validity of a password is drastically shortened.
Another crucial yet often overlooked aspect of password management is the security of question-answer pairs. Ideal security questions and answers are those only the account holder can know. Yet, the proliferation of social media quizzes probing for personal milestones like one’s first car, kindergarten teacher’s name, or childhood street may inadvertently arm cybercriminals with the answers needed to bypass security checks. This underscores the importance of selecting security questions wisely and recognizing the potential risks of engaging in seemingly harmless online quizzes.
5. Use Multi-factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor authentication (MFA), sometimes referred to as two-factor authentication, enhances security by requiring users to pass through multiple verification steps before accessing password-protected systems and applications. This method involves at least two forms of identity verification to ensure a user’s authenticity.
Setting up MFA begins with the traditional step of entering a password on an app or device. Subsequent steps involve additional verification methods, such as:

- Receiving and using a code or clicking a link sent via SMS or email.
- Confirming a login attempt through a notification in a mobile app when attempting to access from a computer.
- Activating a connected device, like pressing a button on a smartwatch.
- Inputting a code from a designated authenticator app.
- Using biometric validation, such as a fingerprint scan.
- Employing a physical authentication tool like the YubiKey by inserting or tapping it.
Opting for an authenticator app, biometric data, or a physical security device offers stronger protection than SMS-based codes, which could be compromised if a phone’s SIM card is stolen, duplicated, or tampered with, potentially leading to data breaches or cyberattacks.
For organizations distributing hardware to staff, incorporating a physical authentication device is straightforward. In scenarios involving bring-your-own-device (BYOD) policies or independent teams, it’s advisable to mandate the use of authentication apps like Google Authenticator or Microsoft Authenticator, enhancing security across all user access points.
6. Regularly Back Up Data
It’s crucial to have a thorough data backup strategy, even with robust physical and electronic security measures in place. Utilizing secure cloud services, like Google Workspace, ensures that important documents are accessible, even if your primary device fails. This approach safeguards against the loss of essential files but doesn’t cover everything.
Backing up additional data such as application settings, contact details, and more to a secure location allows for quick setup of a replacement device exactly to your needs. Both Apple and Windows offer built-in backup solutions to either iCloud or Microsoft accounts, or to a physical external drive. For broader corporate needs, third-party enterprise security systems are available to back up entire computer networks, websites, and more, providing comprehensive protection against ransomware attacks and unforeseen disasters for a smoother recovery process.
7. Be Wary of Social Engineering
Sometimes, social engineers aim to trick your team members into giving away confidential information. This tactic, known as social engineering, involves manipulating individuals to gain unauthorized access to company secrets.9. Stay Informed About Security Trends
The manipulators build trust through various communications, pretending to deal with business matters, or impersonating trustworthy positions such as HR or IT staff.
Your team member, believing they are interacting with a legitimate contact, might unknowingly become a victim of scams like:
- Phishing: Using deceitful links, calls, texts, etc., to infiltrate systems.
- Baiting: Distributing malware via email attachments and other means.
- DNS Spoofing: Hijacking browser traffic to redirect users.
- Scareware: For instance, ransomware demanding payment for system access.
Given that even genuine contacts can be compromised, it’s vital to:
- Evaluate the safety of files and links in emails or texts. Avoid opening anything suspicious, even from known addresses.
- Inspect email and web addresses closely, watching for subtle tricks like a “rn” replacing an “m.”
- Limit information shared with outsiders to what’s strictly necessary.
- Verify the legitimacy of unexpected requests, even from colleagues.
- Confirm the identity of unfamiliar contacts claiming to be colleagues, vendors, or customers.
- Report any data request concerns to higher-ups for verification.
Social engineers count on their targets feeling too overwhelmed or ashamed to seek assistance. If faced with a dubious message or link, always consult with a trusted expert.
Cybersecurity is an evolving field. Staying informed about the latest security trends, threats, and best practices is essential for proactive defense. Encourage your team to continually educate themselves on cybersecurity matters.
The bottom line
In an era where remote work is becoming the norm, proactively addressing the cybersecurity challenges associated with hiring remote developers is essential. By incorporating robust security practices into your operations, you can not only protect your digital assets but also foster a culture of cybersecurity awareness and compliance within your remote teams. This proactive approach ensures that your venture into the global talent pool is both rewarding and secure, keeping your business resilient in the face of evolving cyber threats.






